In the U.S., several utilities have announced life extensions and power uprates of existing, operating reactors because of government policy changes that are directly supporting nuclear power. With several reactor construction projects recently approved and many more planned around the world, demand for uranium fuel continues to increase.

Provides a safe, reliable, and cost effective source of American energy.
The President signed H.R. 1042, the Prohibiting Russian Uranium Imports Act, into law May 13, 2024. This bipartisan legislative action prohibits the import of Russian uranium products into the United States as of August 12, 2024, while enabling a waiver process with the Department of Energy, in consultation with the Departments of State and Commerce, through January 1, 2028, consistent with the law.
On March 8th, 2024, Congress made available to the Department of Energy $2.72 billion to carry out the Nuclear Fuel Security Act of 2023 by establishing and expanding enrichment and conversion services to meet U.S. domestic nuclear fuel requirements while working with our allies and partners in the event of a supply disruption.
In March 2024, President Joe Biden signed into law the Consolidated Appropriations Act of 2024, which, among other priorities, provided $2.72 billion for increasing U.S. domestic nuclear fuel supply chain capacity to meet the needs of U.S. operating nuclear reactors and future reactor designs.
The Civil Nuclear Credit Program is a $6 billion strategic investment through the Bipartisan Infrastructure Law (BIL) to help preserve the existing U.S. reactor fleet and save thousands of high-paying jobs across the country.)
The ADVANCE Act will:
was signed into law by President Biden in April 2024
The National Defense Authorization Act of 2024 includes language backed by Senate Energy and Natural Resources Chair Senator Joe Manchin (D-WV) and ranking member Senator John Barrasso (R-WY), to promote the domestic availability of High-Assay Low-Enriched Uranium (HALEU) to fuel advanced reactors and direct the Department of Energy to create a “Nuclear Fuel Security Program.”
It is the largest source of carbon-free electricity in the United States and protects our air quality by generating electricity without other harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, or mercury.
Despite producing massive amounts of carbon-free power, nuclear energy produces more electricity on less land than any other clean-air source. A typical 1,000-megawatt nuclear facility in the United States needs a little more than 1 square mile to operate. NEI says wind farms require 360 times more land area to produce the same amount of electricity and solar photovoltaic plants require 75 times more space. To put that in perspective, you would need more than 3 million solar panels to produce the same amount of power as a typical commercial reactor, or more than 430 wind turbines (capacity factor not included).
One uranium fuel pellet—about the size of a gummy bear—creates as much energy as one ton of coal, 149 gallons of oil or 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas. A single nuclear power reactor generates enough electricity on average to power over 700,000 homes without emitting any greenhouse gases—that’s more than enough to power a city the size of Philadelphia. In fact, America’s 94 nuclear plants produce enough electricity to power 75 million homes.
Despite common misconceptions, nuclear energy is one of the safest sources and has seen dramatic changes over the last 50 years to make the technology even safer and more efficient.
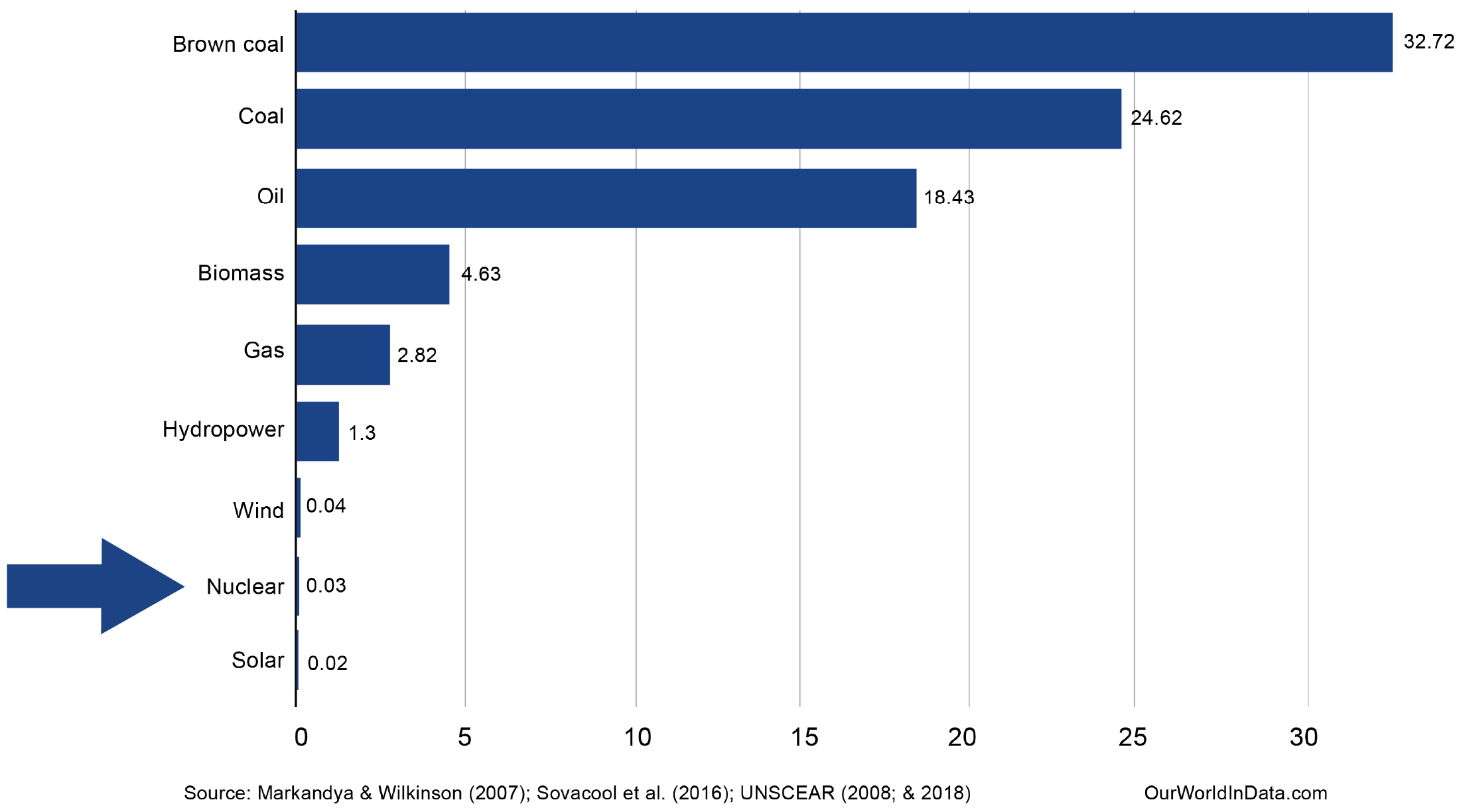
Comparative death rates per unit of electricity production


It is the largest source of carbon-free electricity in the United States and protects our air quality by generating electricity without other harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxide, sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, or mercury.
Despite producing massive amounts of carbon-free power, nuclear energy produces more electricity on less land than any other clean-air source. A typical 1,000-megawatt nuclear facility in the United States needs a little more than 1 square mile to operate. NEI says wind farms require 360 times more land area to produce the same amount of electricity and solar photovoltaic plants require 75 times more space. To put that in perspective, you would need more than 3 million solar panels to produce the same amount of power as a typical commercial reactor, or more than 430 wind turbines (capacity factor not included).



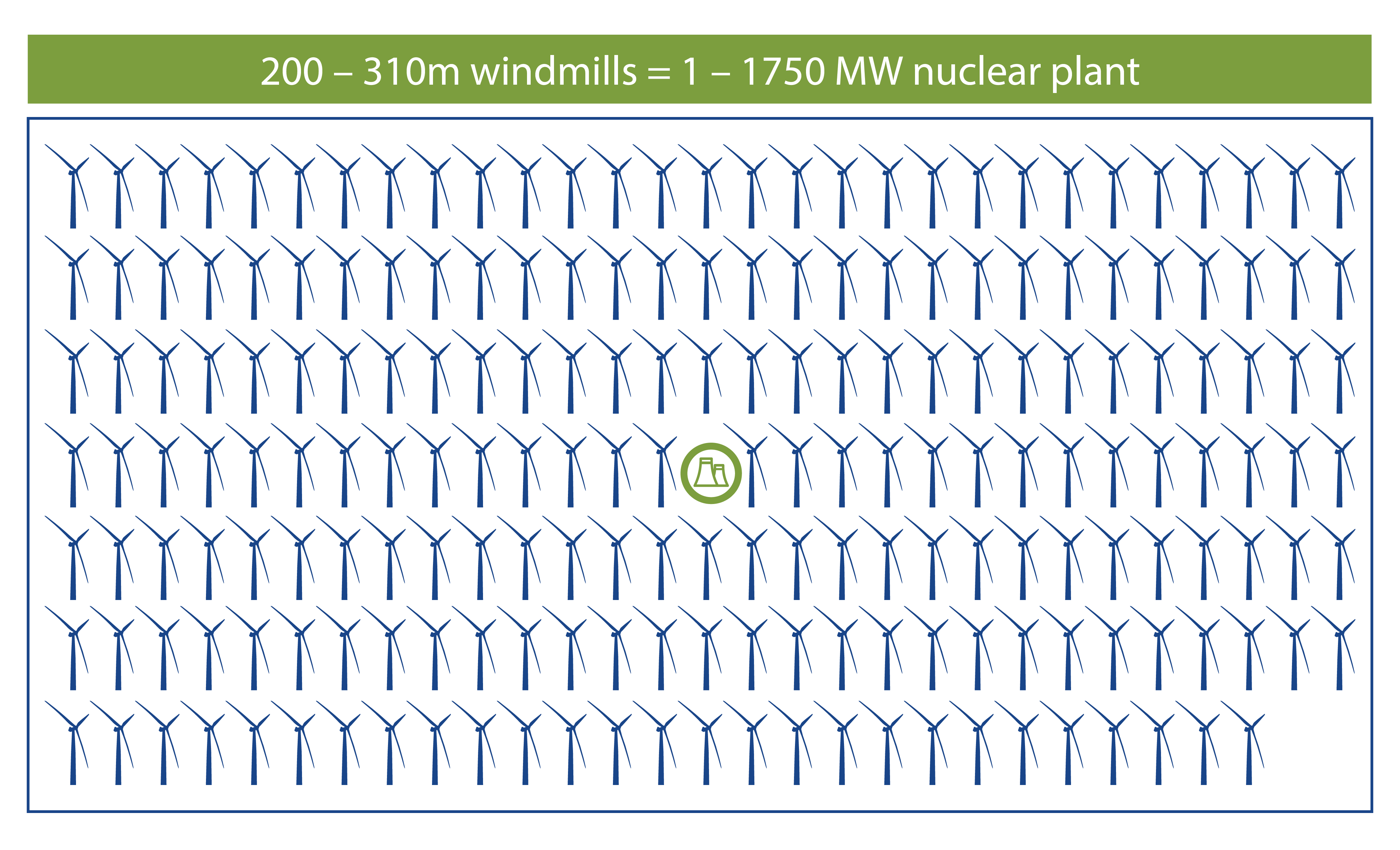


Nuclear is Powerful
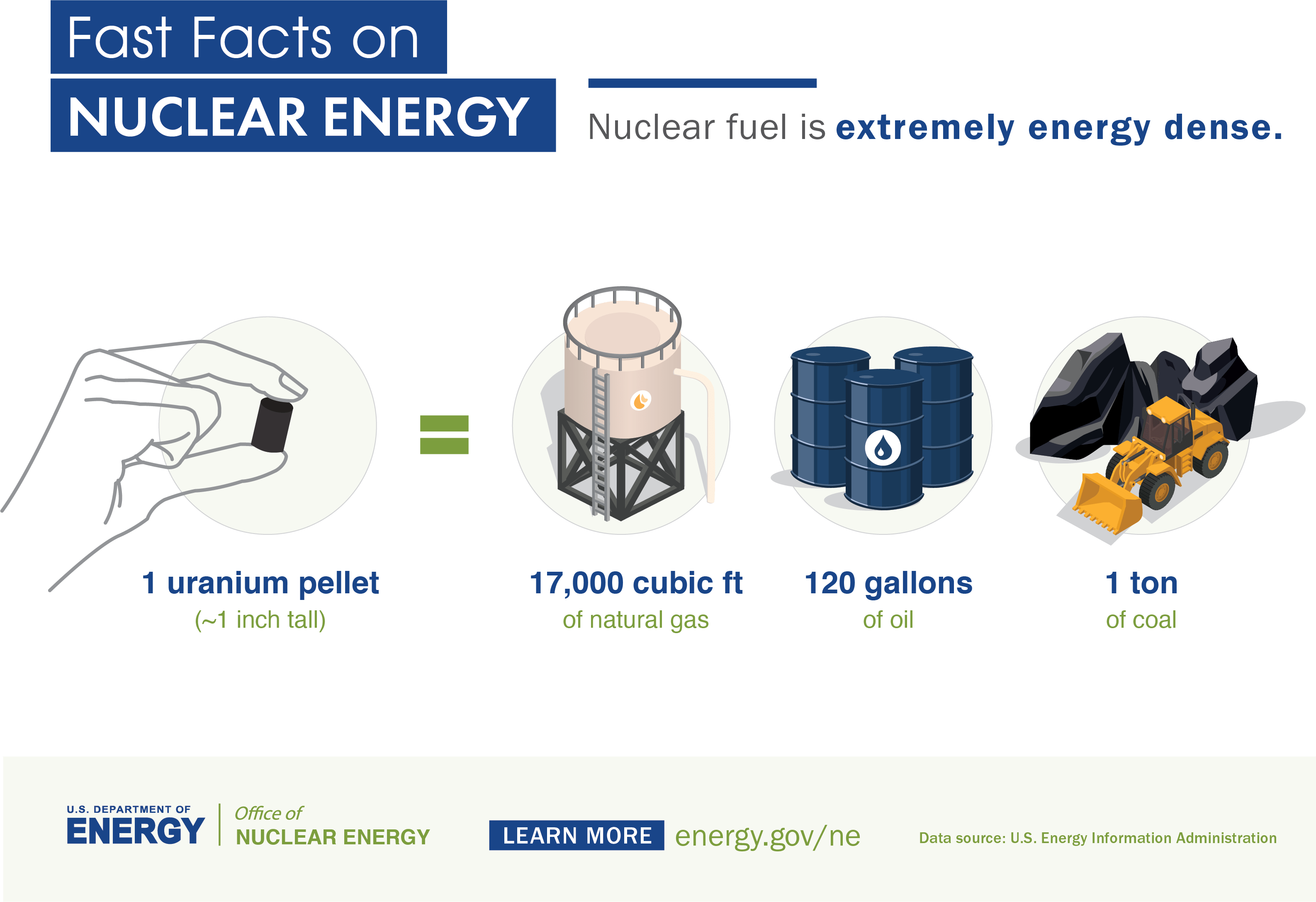


One uranium fuel pellet—about the size of a gummy bear—creates as much energy as one ton of coal, 149 gallons of oil or 17,000 cubic feet of natural gas. A single nuclear power reactor generates enough electricity on average to power over 700,000 homes without emitting any greenhouse gases—that’s more than enough to power a city the size of Philadelphia. In fact, America’s 94 nuclear plants produce enough electricity to power 75 million homes.
Despite common misconceptions, nuclear energy is one of the safest sources and has seen dramatic changes over the last 50 years to make the technology even safer and more efficient.
Comparative death rates per unit of electricity production



Nuclear utility contracting to secure long-term requirements for conversion and enrichment services has continued into 2024
Higher prices across the fuel cycle and annual contracting activity that is getting closer to the rate required to replace what is consumed annually, indicate that utilities are returning their focus to secure the uranium necessary to feed those services.
enCore Energy expects continued competition among utilities to secure long-term contracts for uranium products and services with proven producers who demonstrate strong environmental, social and governance (ESG) performance and from assets in geopolitically attractive jurisdictions on terms that will ensure the availability of reliable supply to satisfy demand.
In both its high and low case scenarios, the IAEA now envisions 25 percent more nuclear energy capacity installed by 2050 than it did as recently as 2020, which underscores how a growing number of countries are looking to nuclear to address the challenges of energy security, climate change, and economic development.
Several non-nuclear countries continue to emerge as candidates for new nuclear capacity
In the European Union (EU), specific nuclear energy projects have been identified for inclusion under its sustainable financing taxonomy and are therefore eligible for access to low-cost financing. In some countries where phase-out policies were previously in place, there have been policy reversals and potential reactor life extensions with public opinion polls showing growing support.
Suite 1020 – 800 West Pender St.
Vancouver, BC V6C 2V6
Nuclear Fuels Inc.
info@nfuranium.com
+1 (778) 819-7477
Suite 1020 – 800 West Pender St. Vancouver, BC V6C 2V6
Nuclear Fuels Inc.
info@nfuranium.com
+1 (778) 819-7477
© 2024 Nuclear Fuels Inc. | Website By Exploration Sites